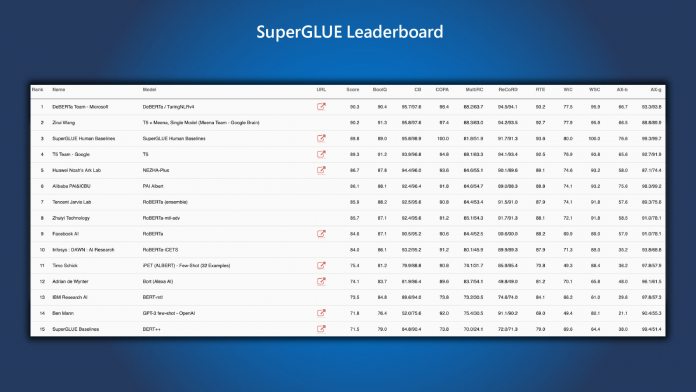
DeBERTa (Decoding-enhanced BERT with disentangled attention) is an AI model that Microsoft has recently updated. The new model has 1.5 billion parameters and 48 Transformer layers. After boosting DeBERTa, Microsoft Research wanted to put the improved model through its paces. Turning to the SuperGLUE benchmark, the results were amazing. In fact, the AI model became the first language processing and understanding AI to beat human performance. DeBERTa got a macro-average score of 89.9, beating the 89.8 that humans can achieve. The model also bested humans in the baseline score (90.3 against 89.8). Microsoft says DeBERTa can outperform rival pretrained language models (PLMs) because of three improvements. The company added an enhanced mask decoder, a disentangled attention mechanism, and a virtual adversarial training method.
Major Step Forward
In its blog post, Microsoft points out how the new improvements are a step forward for PLM research: “DeBERTa sets new state of the art on a wide range of NLU tasks by combining the three techniques detailed above… DeBERTa surpassing human performance on SuperGLUE marks an important milestone toward general AI.” Looking at Google’s T5 AI by comparison, it only has 11 billion parameters. That may seem better on paper, but more is not better in this case. That’s because the 1.5 billion parameters of DeBERTa makes it much more energy efficient. It also makes carrying out tasks such as compressing, deployment, and maintenance easier. Moving forward, Microsoft says the source code will be made publicly available, as well as open-source access to the DeBERTa model. On the company’s side, the AI will be folded into the next release of the Microsoft Turing natural language representation model (Turing NLRv4). Tip of the day: Did you know that Windows 10´s Task Manager lets you set CPU affinity to claw back some resources from running apps and give selected apps higher priority. Our tutorial shows how you can use this helpful feature.